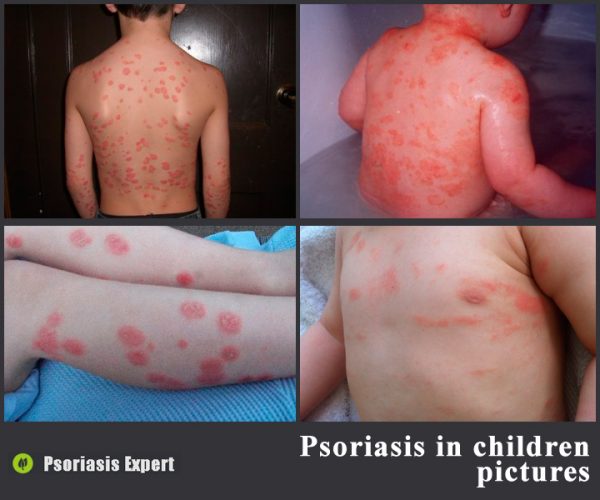
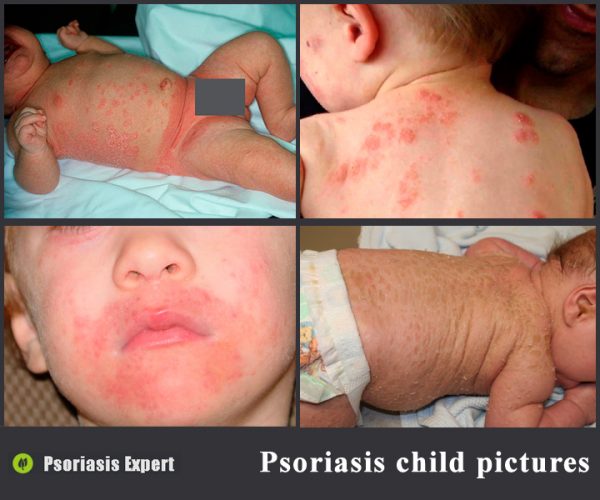
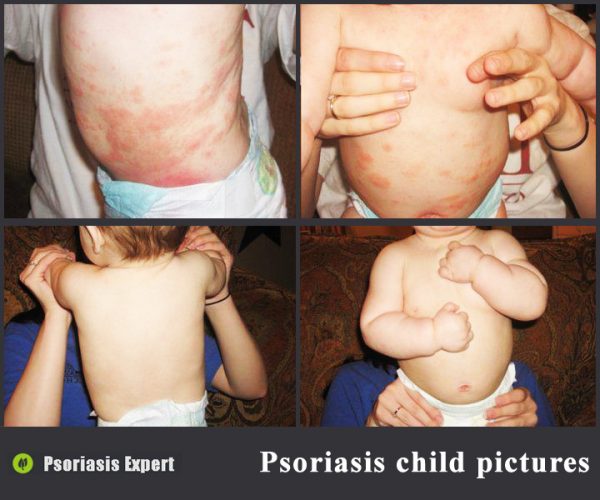
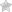Psoriasis in children is a common disease. The causes of this pathology are similar to the factors that cause the disease in adults. However, the symptoms in children and the treatment are somewhat different.
The dermis cells of a healthy person have a tendency to renew every 28-30 days. With psoriasis, this process accelerates and the excessive formation and division of cells is perceived by the immune system as an aggressor which results in a strong inflammatory process. The skin goes red, round and oval spots rising for 2-3 mm above its surface become noticeable. Patients suffer from a strong feeling of itching and discomfort.
Psoriasis in children – both in infants and in adolescents – is most often caused by hereditary factor. If any of the parents had previously been diagnosed with this disease, then the likelihood of developing the pathology in their child is very high.
The signs of psoriasis in children are almost the same as in adults. The disease is most often located in the following places:
- groin;
- buttocks;
- lower back;
- in places of contact of the diaper with the skin;
- on the head;
- in the armpits.
There is no need to pass serious laboratory tests to diagnose psoriasis in children. Most often, a visual examination and a couple of questions to the parents is more than enough. Sometimes a biopsy of skin samples is required in cases where the disease patterns are not clear.
Why causes psoriasis in children?
The main causes of pathological factors are the following:
- Genetic predisposition is considered to be one of the most important factors affecting the development of the disease – 60% of cases.
- Emotional burnout. Non-compliance with the healthy regime, poor sleep of the child, as well as excessive excitement can also provoke the development of the disease.
- Various allergic reactions. It can be food, plant pollen, hygiene products, pet hair, and even ordinary dust.
- Congenital and acquired diseases of the endocrine system. The diseases of such organs as the thyroid gland and pancreas often cause the disorder of hormonal balance which also contributes to the development of psoriasis.
Psoriasis in children under a year
This disease is often found in very young children. Psoriasis in children under 1 year of age can be caused by the following factors:
- genetic predisposition to the disease;
- infectious diseases caused by streptococcus lead to the reaction of the immune system resulting in this disease;
- stresses caused by fear;
- cold season, the absence of direct sunlight and dry air negatively affect the skin;
- vaccinations can cause an allergic reaction in the form of psoriasis.
In addition to these causes, the disease can be provoked by yet weak immunity. The treatment of the affected skin involves the compliance with hygiene norms, as well as local treatment with moisturizing ointments, creams, lotions.
Symptoms
Psoriasis in children and its symptoms may differ slightly depending on the type and severity of the pathology. For example, in infants, the disease is most often characterized by the appearance of pink and red spots that slightly rise above the surface of the skin. Peeling and severe itching are absent.
How does psoriasis in children start? Pustular psoriasis may lead to rashes on the body of a child in the form of vesicles filled with liquid. After they burst, red non-healing spots remain on the body.
Very often, when a kid scratches a wound it also adds bacterial infection to the list of problems. This greatly aggravates the course of the disease and requires serious treatment.
Plaque psoriasis usually reveals itself with flaky itchy spots that have a bright red color. During the development of the disease, the spots merge with each other forming large lesions. The skin in such places is irritable and sensitive, even minor mechanical damages can provoke bleeding.
Stages of child psoriasis
The disease develops in several stages, each of them have their own symptoms. These include the following periods:
- Latent stage. This period is characterized by the appearance of signs that signal the imminent occurrence of the disease.
- Progressing stage. At this stage, the kid notices rashes and other signs of the disease.
- Remission stage. The main manifestations of the disease disappear, and a so-called period of lull begins.
- The relapse. Relapse is the recurrence of pathology.
The correct and timely treatment determines on the duration of remission. With proper therapy, this period can last several years, in other cases the disease might not disappear at all – local rashes stay on the body for years.
Doctors also divide children’s psoriasis at the following stages:
- Progressing.
- Stationary.
- Regressive.
Progressive form is characterized by the appearance of plaques and papules, severe itching, and redness. At the stationary stage, the symptoms somewhat decrease, but psoriatic rashes continue to appear. At the stage of regression, the skin clears, symptoms go away, and a period of remission begins.
Types of psoriasis in children
Psoriasis in children with difficult and long-term treatment is divided into several types, depending on the symptoms and features of the course. They include:
- Plaque psoriasis. One of the most frequent forms of the disease. It is characterized by the appearance of red spots, accompanied by peeling and itching. These spots can be as large as a few centimeters and much larger.
- Guttae psoriasis in children. One of the most common dermatological diseases in children. This form of the disease develops as a result of minor damage of the skin, which is converted into small bumps of red hue. After a while, such wounds begin to peel off. This process is accompanied by severe itching. Very often the parents of affected children confuse the guttae form of the disease with an allergy which is why they do not immediately turn to a specialist.
- Pustular psoriasis. Characterized by the appearance on of the bubbles filled with liquid. The formations burst, exposing the inflamed skin.
- Generalized psoriasis. It arises abruptly and affects extensive areas of the skin. Often entails serious complications in the form of diseases of the kidneys, heart and other organs.
- Inverse psoriasis. It occurs most often in the area of the elbows and knee joints. The disease might also manifest itself in the groin and underarms. It appears as red spots.
- Erythrodermic psoriasis. It affects large areas of the skin with its subsequent peeling. Very dangerous type of the disease that can lead to death.
- Arthropathy psoriasis. It is quite rare, but still possible in childhood. It manifests itself in general deterioration of the patient’s condition, muscular and joint pain. The fingers and toes can swell, and conjunctivitis is also a common symptom.
Psoriasis in children: the initial stage
Psoriasis is not a contagious disease. It can be caused by the following factors:
- hereditary predisposition;
- infectious diseases;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- disturbance of metabolic processes.
The initial stage of psoriasis in children is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- minor rashes localized on the face, head, behind the ears, on the neck, in the skin folds;
- the rash is concentrated in places with injuries, bruises, scratches and other damages;
- severe itching in the affected areas.
The disease in children manifests itself very quickly – a lot faster than in adults.
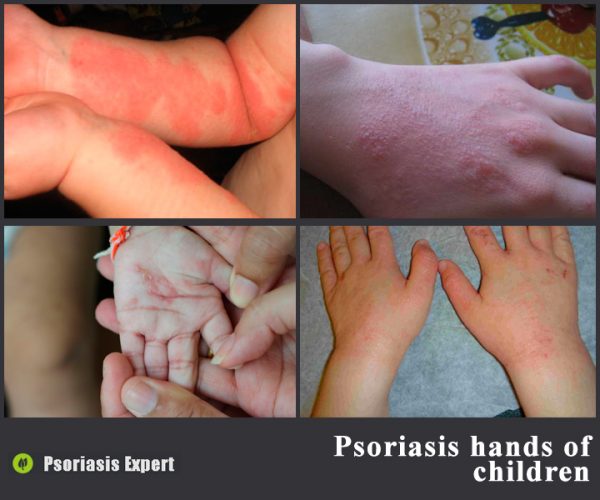
Psoriasis on the hands of children
This disease very often affects the skin of the hands and fingers in children. Pathology develops as a result of the following irritating factors:
- allergic reactions to food, household chemicals, hygiene items;
- emotional stress which makes the child injure the skin of his or her hands;
- metabolic disorders;
- weakened immune system;
- pathology of internal organs.
As for adolescents, the affection of the upper limbs is usually the result of hormonal changes in the body.
Basic principles of treatment of psoriasis in children
Next, we will try to figure out how to treat psoriasis in children. The first thing that parents should do is to go to the clinic for the correct diagnosis. Only there an experienced specialist will be able to prescribe all necessary drugs and therapy.
To remove itching, a specialist can prescribe antihistamines.
Small amounts of tranquilizers and hypnotics help to normalize the psychosomatic state. These can be synthetic drugs, as well as herbal remedies.
Local treatment usually involves various creams and ointments. They include:
- salicylic ointment;
- zinc ointment;
- tar soap and cream;
- ointments based on solidol and other substances.