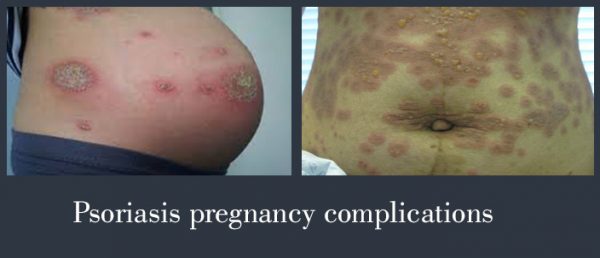
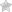Pregnancy may contribute to the development of new diseases and aggravation of the existing ones. One of them is psoriasis during pregnancy, which can develop against the background of hormonal changes in woman’s body.
The mechanism of changing the condition of women suffering from psoriasis during pregnancy is not fully understood. There are cases when the pregnancy became the cause of the development of the primary psoriasis and aggravation of the existing one. However, there are other cases when after the impregnation patient started to feel much better forgetting about acute attacks of the disease.
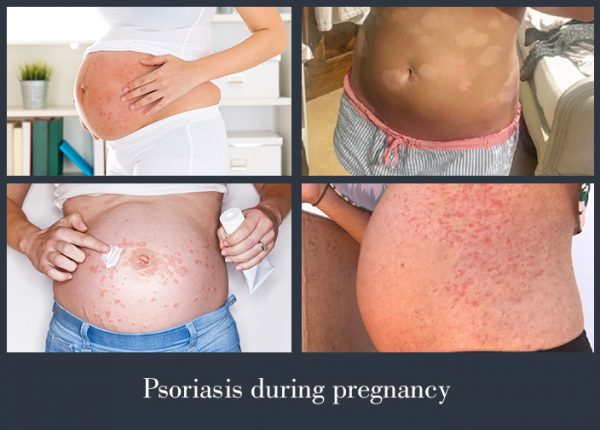
Despite the fact that psoriasis is quite rare in the period of gestation, the aggravation of the disease in this period is most dangerous as it may lead to premature termination of pregnancy, as well as to baby’s hypotrophy after birth.
It is particularly important to observe pregnancy in the development of psoriasis in the first trimestre.
The nature of the development of psoriasis indicates the course of the remaining period and pregnancy outcomes.
It is dermatologist alongside with gynecologist, who should evaluate patient’s condition, conduct full examination and, if necessary, order the treatment.
Psoriasis is not an infectious disease. Therefore, natural breastfeeding is not dangerous, and even vice versa – it is welcomed, as baby gets all the necessary microelements and nutrients with mother’s milk.
Psoriasis and pregnancy: the treatment during this period
The selection of medications which may be used minimize psoriasis during pregnancy is relatively small. Most drugs usually have toxic effects on baby. It is necessary to take into account that during pregnancy the disease can proceed in a lighter form which allows minimizing drug treatment. Moisturizing ointment might be prescribed in order to prevent skin drying.
The treatment is divided into local and systemic
Local treatment
Since most of systemic drugs are not used during pregnancy, the main attention is put to local medications (ointment, cream, gel):
- nevertheless, even ointment and other topical preparations have some side effects since they can be absorbed through the skin. Some of these drugs are contraindicated for use by pregnant women, as they can cause a teratogenic effect (embryo development disorder);
- the only remedies that can not harm mother and her child are softening creams and ointments. In other cases, the treatment is carried out on limited areas of skin. Softening preparations (moisturizing and softening creams) can be used without any danger. Salicylic acid, which has a good exfoliating effect, can be used on a limited area of the skin;
- during pregnancy, all agents with vitamin A are contraindicated (it has to do with teratogenic action). Preparations with vitamin D can be used in limited quantities.
In rare cases doctor can prescribe corticosteroid drugs. It should be borne in mind that steroid ointment can cause stretch marks, so they are not applied to areas of the body that are prone to the appearance of stretch marks (chest, hips, stomach and buttocks).
System treatment
Treatment with systemic drugs is carried out with caution since many of them are capable of having a pathological effect on fetus, especially when used in the first 3 months of pregnancy, when all the organs and systems of the baby are being developed. During the intake period of some psoriasis medications, doctors recommend using contraceptives and planning the pregnancy no earlier than 2-3 months after the end of the treatment course. Consult your physician on this matter.
Women need to go outdoors, adhere to a diet, and avoid stressful situations.